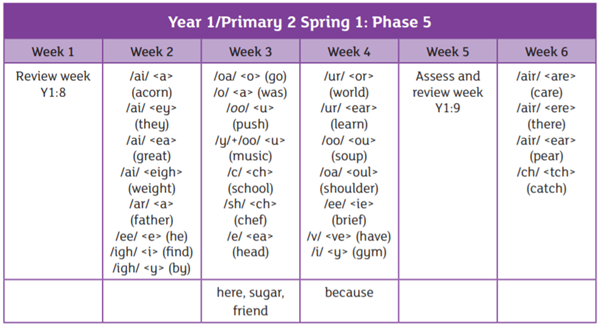
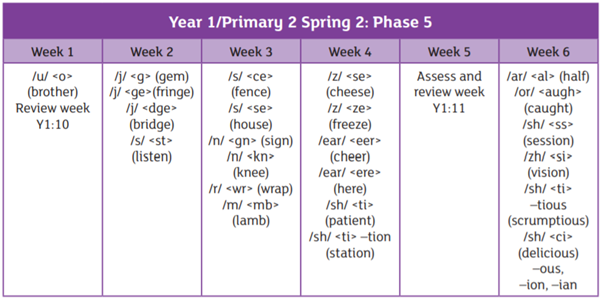
This page should have all the answers you are looking for. It will show you how to say each sound, which terminology to use and what is taught in school. If you have any questions, please speak to your child’s class teacher.
Phonics is recommended as the first strategy that children should be taught in helping them learn to read and write. It runs alongside other teaching methods such as guided reading to help children develop all the other vital reading skills and hopefully give them a real love of reading.
Phonics consists of teaching the skills of segmenting for spelling and blending for reading. Simply put, it is hearing the sounds in a word and writing them down to spell it correctly. When reading, it is sounding out a word and sticking the sounds back together to read the whole word.
Phoneme
A phoneme is the smallest unit of sound in a word.
Feel/watch how your mouth changes when you say a word, every time your mouth moves/changes shape you are saying a new phoneme, e.g. b-r-i-ck
There are 44 phonemes in the English language
Grapheme
A grapheme is a letter or a number of letters that represent a sound (phoneme) in a word. A three letter grapheme could be igh in the word b-r-igh-t. There are 3 letters that make one phoneme..
A grapheme can represent more than one phoneme e.g. C = cat and city
Diagraph
Two letters, which makes 1 phoneme. e.g. d-u-ck
A consonant diagraph contains two consonants
e.g. sh ck th ll
A vowel diagraph contains at least one vowel
e.g. ai ee ar oy
Split Diagraph
A diagraph in which the two letters are not adjacent e.g. make
a-e is a unit of sound (diagraph)- it is being ‘split’ by the constant k.
Trigraph
Three letters, which make 1 phoneme. e.g. l-igh-t
Oral blending
Hearing a series of spoken phonemes and merging them together to make a spoken word without corresponding to any graphemes (no text is needed). e.g. teacher says “b-u-s” children say “bus”
Blending
Recognising the letter sounds in a written word and merging them together in the order they are written to pronounce the word. e.g. c-u-p = cup
Segmenting
Identifying the individual phonemes in a spoken word and writing them down to form a word.
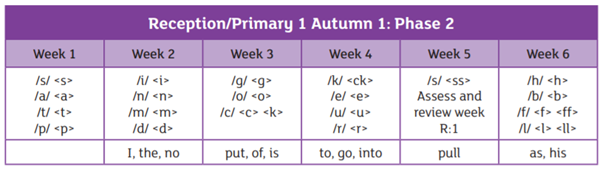
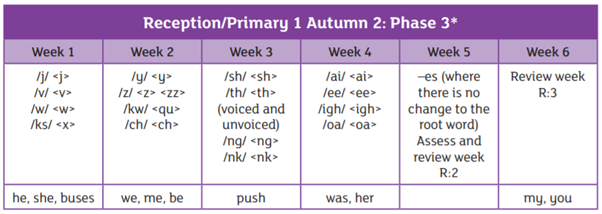
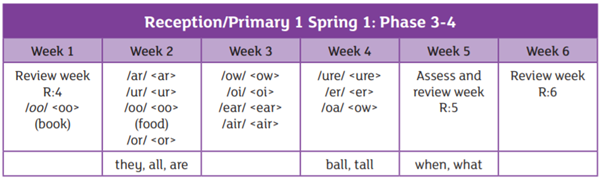
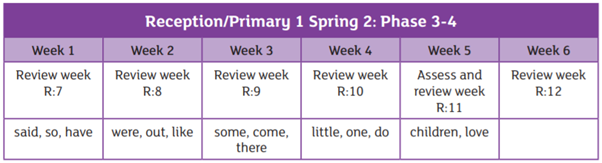
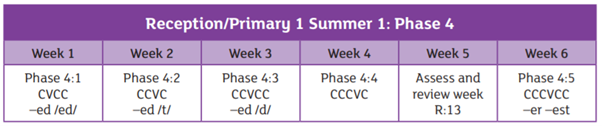
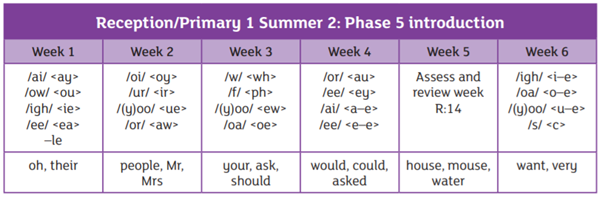
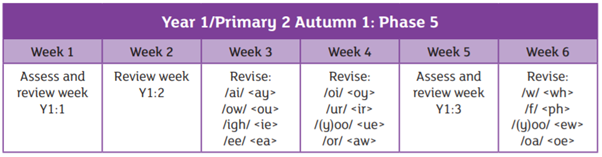
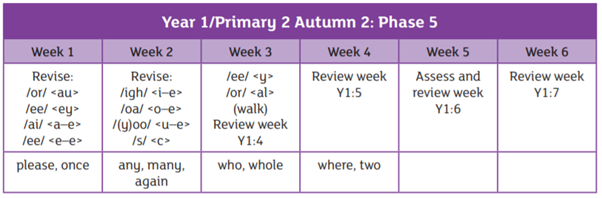
We are using the Essential Letters and Sounds programme to teach phonics in school. This is an accredited systematic synthetic phonics programme aimed at getting all children to read well and quickly. The children in Reception and Year 1 have a daily phonics lesson to teach them the skills they need to read and write.
You can find out more about ELS and how to support your child with reading at home by watching this video.
There are games you can play online at letters-and-sounds.com which will help your child practice their phonics skills in a fun way.
Please take time to do these with your child as it will make a huge different to their progress.
You can find out how to pronounce the letter sounds correctly here.